Handling Chemicals, Hazardous Substances & Dangerous Goods
Handling Chemicals, Hazardous Substances & Dangerous Goods | JSEAsy Australian WHS guidance for handling chemicals, hazardous substances and dangerous goods. Risk assessments, SDS, storage, controls and procedures.


Safe Handling of Chemicals, Hazardous Substances and Dangerous Goods
Managing chemicals, hazardous substances, and dangerous goods safely is a critical responsibility for workplaces worldwide. Australian workplaces must manage chemical risks in accordance with WHS legislation. Improper use, storage, or disposal can result in serious injuries, health risks, fires, explosions, and environmental harm.
JSEAsy provides practical, internationally-relevant documentation to help organisations identify chemical hazards, assess risks, and implement effective controls to maintain a safe working environment.
What Are Chemicals, Hazardous Substances and Dangerous Goods?
Chemicals
Chemicals include any substance, mixture, or product used or generated at work, such as fuels, solvents, acids, cleaning agents, adhesives, paints, gases, and industrial chemicals.
Hazardous Chemicals / Substances
Hazardous chemicals are substances classified as posing health or physical risks. They may cause:
Acute or chronic health effects (toxicity, sensitisation, carcinogenicity)
Skin or eye irritation or burns
Long-term occupational illnesses
Examples include solvents, pesticides, corrosives, silica-based products, and isocyanates.
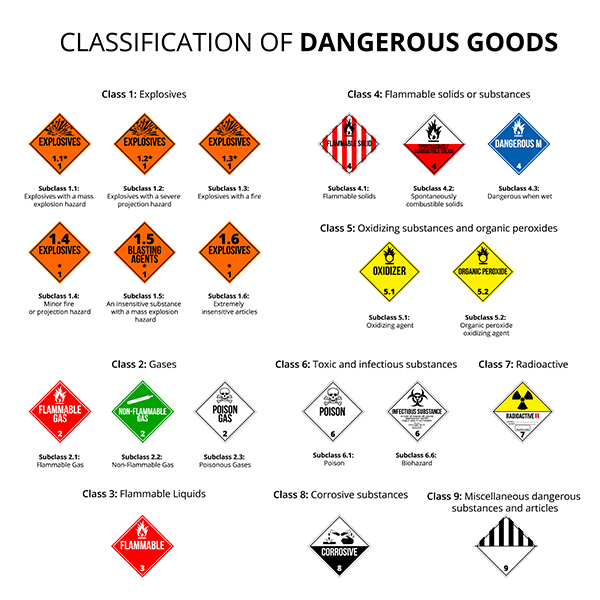
Dangerous Goods
Dangerous goods are chemicals that present immediate physical hazards, including:
Flammability
Explosiveness
Oxidising properties
Corrosivity
Acute toxicity
They are classified by internationally recognised hazard classes and require careful storage, labelling, and segregation.

Key Risks Associated With Handling Hazardous Chemicals and Dangerous Goods
Common risks when handling hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods include:
Inhalation of fumes, vapours, mists, or dusts
Skin or eye contact causing burns or dermatitis
Fire or explosion from ignition of flammable substances
Chemical reactions from incompatible storage
Environmental contamination from spills or leaks
Improper disposal or uncontrolled releases
Without effective controls, these risks can lead to serious injuries, long-term health impacts, and business disruption.
Legal and Safety Obligations (Australia)
Under Australian WHS legislation, persons conducting a business or undertaking (PCBUs) must, so far as is reasonably practicable:
- Identify hazardous chemicals used, handled, stored, or generated
- Eliminate risks or minimise them using the hierarchy of control
- Ensure chemicals are correctly labelled and accompanied by Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
- Maintain a hazardous chemicals register
- Provide appropriate storage, segregation, and spill containment
- Train workers in safe handling, emergency response, and use of PPE
- Implement emergency procedures for spills, leaks, fires, and exposures
Specific additional duties apply to high-risk hazardous chemicals and large quantities of dangerous goods.


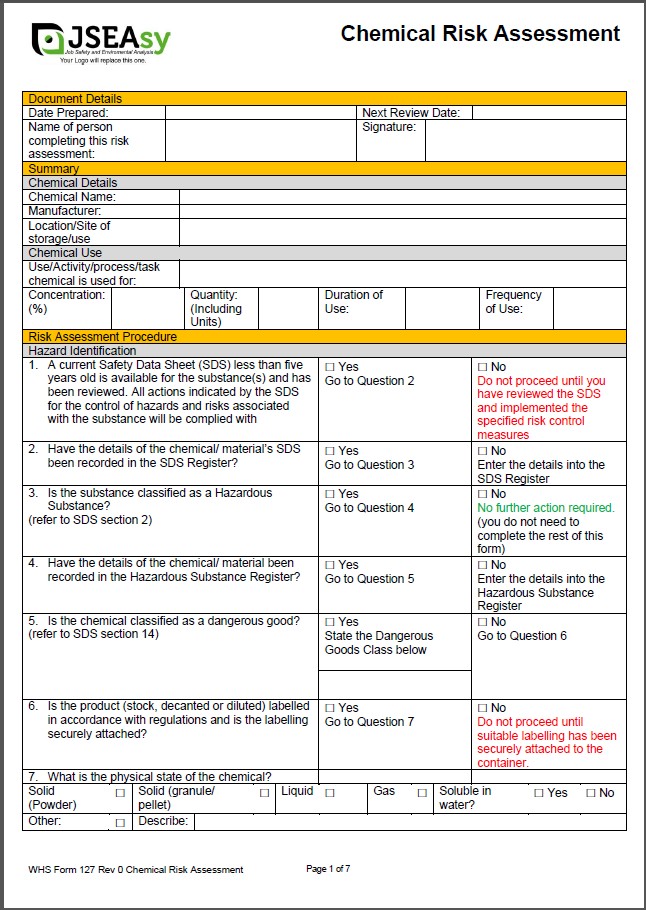
Managing Chemical Risks – Best Practice WHS Approach
1. Identification and Classification
Identify all chemicals in the workplace
Confirm hazard classifications and SDS
Document quantities, use, and storage
2. Risk Assessment
Assess exposure pathways (inhalation, skin contact, ingestion)
Evaluate quantities, frequency, and environmental factors
Consider storage, transport, and disposal risks
3. Control Measures
Apply the hierarchy of control:
Eliminate or substitute hazardous chemicals where possible
Use engineering controls (ventilation, bunding, closed systems)
Apply administrative controls (procedures, signage, permits)
Provide personal protective equipment (PPE)
4. Storage and Labelling
Store chemicals in approved containers and cabinets
Segregate incompatible substances
Maintain clear labelling and signage
Provide secondary containment as needed
5. Training and Supervision
Educate workers on hazards and SDS information
Train workers in handling, spill response, and emergency procedures
Supervise high-risk chemical tasks
6. Emergency Preparedness
Use appropriate spill kits
Provide eyewash stations and safety showers where required
Ensure fire protection and isolation controls
Implement incident reporting and investigation processes
Chemical Safety Documentation and WHS Templates from JSEAsy
JSEAsy provides practical, editable documentation to support chemical safety worldwide, including:
- Hazardous chemical risk assessments
- Dangerous goods handling procedures
- Storage and segregation guides
- Spill response and emergency procedures
- Safe Work Method Statements (SWMS)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA)
- Job Hazard Analysis (JHA)
- Registers and checklists aligned with international standards
Our documents are designed to be practical, editable, and suitable for site-specific use across Australian workplaces.

Why Choose JSEAsy for Chemical Safety
Developed with international safety standards and Australian WHS legislation in mind
Practical, site-ready documentation
Easy to customise for specific operations
Supports compliance and due diligence obligations
Saves time while improving workplace safety
If your business handles chemicals, hazardous substances, or dangerous goods, having clear and compliant procedures is essential. JSEAsy helps you implement effective controls, meet WHS obligations, and demonstrate due diligence in chemical safety management.


Industries and Workplaces We Support
Our chemical safety resources are suitable for:
Construction and civil engineering
Maintenance and facilities management
Manufacturing and industrial operations
Utilities and infrastructure projects
Workshops, depots, and warehouses
Any workplace using, storing, or transporting hazardous chemicals or dangerous goods
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods?
Hazardous chemicals pose health risks, while dangerous goods present immediate physical hazards like fire, explosion, or corrosion. Some chemicals may be classified as both.
Do I need a hazardous chemicals register?
Yes. Australian WHS regulations require workplaces to maintain a register of hazardous chemicals, including current Safety Data Sheets (SDS), where workers may be exposed.
When is a chemical risk assessment required?
Whenever hazardous chemicals are used, stored, or handled, especially if there is potential risk to health or safety.
What documents should I have for chemical safety?
Common documents include chemical risk assessments, hazardous chemical registers, SDS, storage and segregation procedures, spill response plans, and SWMS or JSEAs for high-risk activities.
Are dangerous goods subject to additional requirements?
Yes. Dangerous goods are subject to specific classification, storage, segregation, labelling, and emergency response requirements depending on quantity and hazard class.

